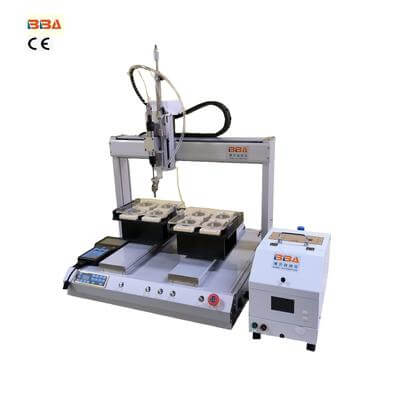
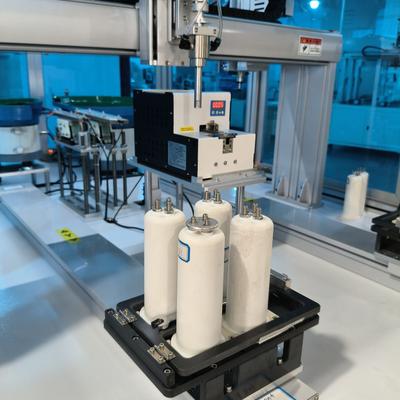
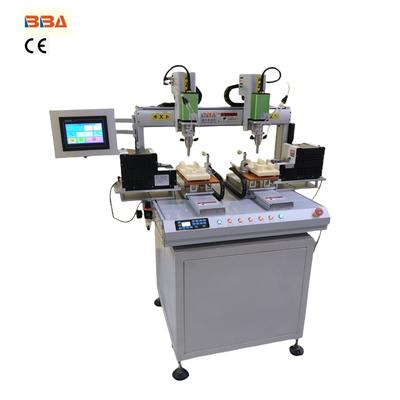
Smart Screw Driving Machine | Industrial Automation for Toy Manufacturing
In the world of industrial automation, screw driving machines represent a fascinating intersection of precision engineering and robotics. These devices, often overlooked in discussions about advanced manufacturing, play a critical role in assembly lines across industries. By combining mechanical ingenuity with intelligent control systems, modern screw driving machines have evolved far beyond their manual predecessors, delivering unmatched speed, accuracy, and adaptability.
At their core, screw driving machines automate the process of fastening screws into components with exact torque control. What makes them truly remarkable is their integration of robotic principles. A typical system comprises three key elements: a robotic arm or linear motion system for positioning, a torque-controlled screwdriver unit, and a vision or sensor system for real-time feedback. The synchronization of these components enables the machine to perform tasks ranging from simple single-screw applications to complex multi-axis operations requiring sub-millimeter precision.
Modern iterations leverage advanced algorithms to optimize screw placement paths dynamically. Machine learning models can analyze historical data to predict optimal torque settings for different materials, reducing the risk of stripped threads or component damage. Some systems incorporate force-torque sensors that mimic human tactile sensitivity, allowing the machine to detect cross-threading incidents and automatically initiate corrective actions. This sensory feedback loop transforms the machine from a simple automaton into an adaptive problem-solving tool.
The integration of collaborative robotics (cobots) has further expanded applications. Unlike traditional industrial robots requiring safety cages, cobot-mounted screw drivers can work alongside human operators, using proximity sensors and torque limiters to ensure safe interaction. This hybrid approach combines human dexterity for complex part positioning with robotic consistency for repetitive fastening tasks, particularly valuable in small-batch production environments.
Energy efficiency represents another frontier in screw driving automation. Newer models employ regenerative braking systems that capture kinetic energy during deceleration phases, repurposing it to power subsequent operations. Variable-frequency drives optimize motor performance based on real-time load requirements, reducing energy consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional systems. These innovations align with growing industry demands for sustainable manufacturing practices.
As industries increasingly adopt smart factory concepts, screw driving machines are evolving into IoT-enabled devices. Embedded sensors collect performance metrics that feed into predictive maintenance systems, alerting technicians about worn components before failures occur. Cloud connectivity allows remote monitoring of torque consistency across multiple production lines, enabling real-time quality assurance adjustments. This data-driven approach not only minimizes downtime but also creates opportunities for continuous process optimization through big data analytics.
The future of screw driving automation points toward even greater cognitive capabilities. Research prototypes now testing computer vision systems with 3D object recognition can identify and fasten screws on irregular surfaces without pre-programmed coordinates. Another emerging trend involves swarm robotics, where multiple compact screw driving units collaborate on large assemblies through decentralized coordination algorithms. These advancements promise to redefine assembly line flexibility, enabling manufacturers to rapidly adapt to product design changes without costly retooling.
From consumer electronics to aerospace manufacturing, the robotics behind screw driving machines continues to push the boundaries of what automated assembly can achieve. As these systems grow more intelligent and interconnected, they will play an increasingly vital role in enabling high-mix, low-volume production models while maintaining the precision and reliability required for mission-critical applications. The humble screw, paired with cutting-edge robotics, remains at the heart of manufacturing innovation.
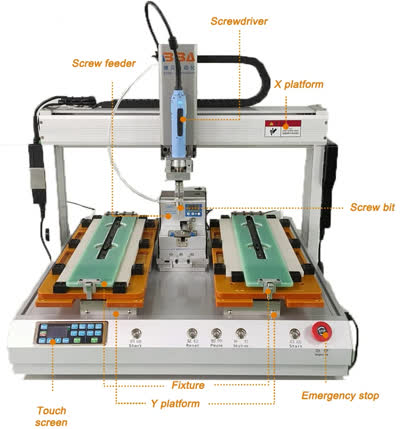
| Product Name | Applicable industries |
| Smart Screw Driving Machine | Toy and Game Console Production |


